Deadlock In Operating System
Deadlock is a situation in a multi-process or multi-threaded system where two or more processes are permanently blocked, because each process is waiting for a resource held by another process as a result, none of the processes can proceed.
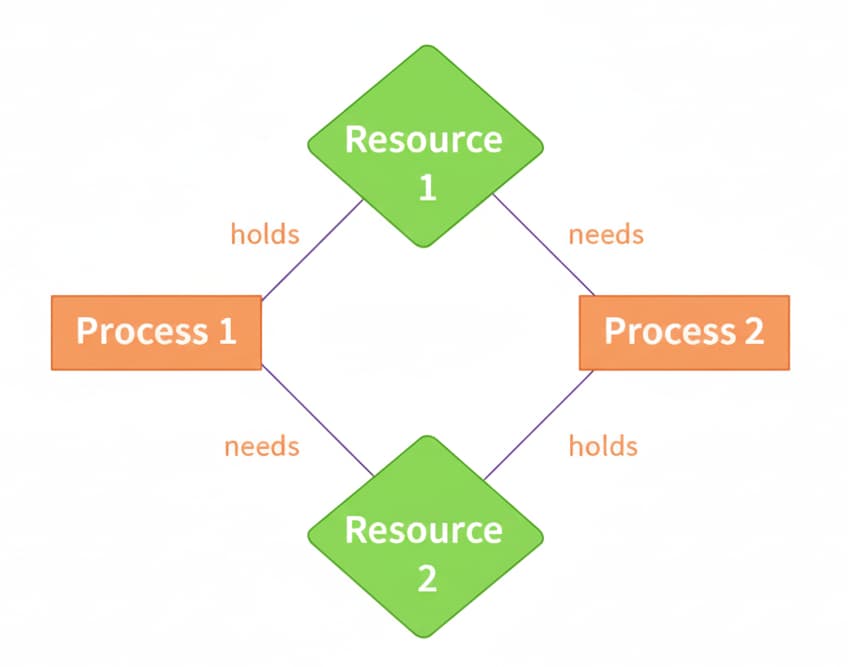
- Process P1 holds Resource A and waits for Resource B.
- Process P2 holds Resource B and waits for Resource A.
Neither can move forward → deadlock.
Conditions for Deadlock(Coffman’s Conditions)
Deadlock can occur only if all four of these conditions hold simultaneously:
- Mutual Exclusion: Only one process can use a resource at any given time i.e. the resources are non-sharable.
- Hold and Wait: A process is holding at least one resource at a time and is waiting to acquire other resources held by some other process.
- No Preemption: A resource cannot be forcibly taken; it must be released voluntarily.
- Circular Wait: A set of processes are waiting for each other in a circular fashion. For example, lets say there are a set of processes (P0,P1,P2,P3) such that P0 depends on P1, P1 depends on P2, P2 depends on P3 and P3 depends on P0. This creates a circular relation between all these processes and they have to wait forever to be executed.
Deadlock is possible only when all four are true. Breaking any one condition prevents deadlock.
Deadlock Handling Methods:
Deadlock prevention is a strategy used in computer systems to ensure that different processes can run smoothly without getting stuck waiting for each other forever.
As we have already discussed that deadlock can only happen if all four of the following conditions are met simultaneously: Mutual Exclusion, Hold and Wait, No Preemption, Circular Wait.
So we can prevent a Deadlock by eliminating any of the above four conditions. Let's look at how:
1. Deadlock Prevention:
Deadlock prevention is a strategy in operating systems where we design the system so that at least one of the four necessary conditions for deadlock can never occur.
- Force all processes to request all resources at once (no hold & wait).
- Impose a strict ordering of resource acquisition (break circular wait).
- Allow the system to preempt resources when needed.
Suppose a process needs CPU, Disk, and Printer.
- System enforces order: CPU → Disk → Printer.
- Process must request CPU first, then Disk, then Printer.
- No circular waiting can occur because all processes follow the same order.
2. Deadlock Avoidance:
Deadlock avoidance means the system monitors and checks every resource request to ensure it never enters an unsafe state. Deadlock avoidance is a strategy in which the operating system carefully checks every resource request and grants it only if it will keep the system in a safe state (i.e., deadlock cannot occur).
- Algorithms like the Banker’s algorithm and Resource Allocation Graph are classic methods to achieve this, providing a balance between flexibility and safety.
- It is more flexible than deadlock prevention—resources can still be allocated dynamically.
3. Deadlock Detection and Recovery:
Sometimes it is not practical to prevent or avoid deadlocks (for example, when processes do not know their maximum future resource needs). In such cases, an operating system can let deadlocks occur, then detect and recover from them. This strategy is called deadlock detection and recovery.
Deadlock detection and recovery is a strategy where the OS allows deadlocks to occur, then finds and resolves them—typically by aborting processes or preempting resources—so the system can continue running.
Let deadlocks happen but detect and fix them:
- Use a wait-for graph to detect cycles.
- Once detected, recover by: Terminating one or more processes, or Preempting resources.
4. Ignoring Deadlock:
Ignoring deadlock means the operating system takes no action to prevent, avoid, or detect deadlocks. In the method, the system assumes that deadlock never occurs. Since the problem of deadlock situation is not frequent, some systems simply ignore it. Operating systems such as UNIX and Windows follow this approach. However, if a deadlock occurs we can reboot our system and the deadlock is resolved automatically.