Computer Networks Introduction
Computer Networks are systems that connect multiple computers and devices so they can communicate, share data, and use shared resources like printers, storage, and the internet.
Before starting, we need to understand some basic terminologies.
What is Data?
Data is simple facts, figures, or observations that we collect, but they don’t have meaning until we understand or process them. In computing, data is information that has been translated into a form that is efficient for movement or processing.
What is communication?
Communication is the process of exchanging information by speaking, writing or using some other medium between two or more people or devices.
Key Elements of Communication
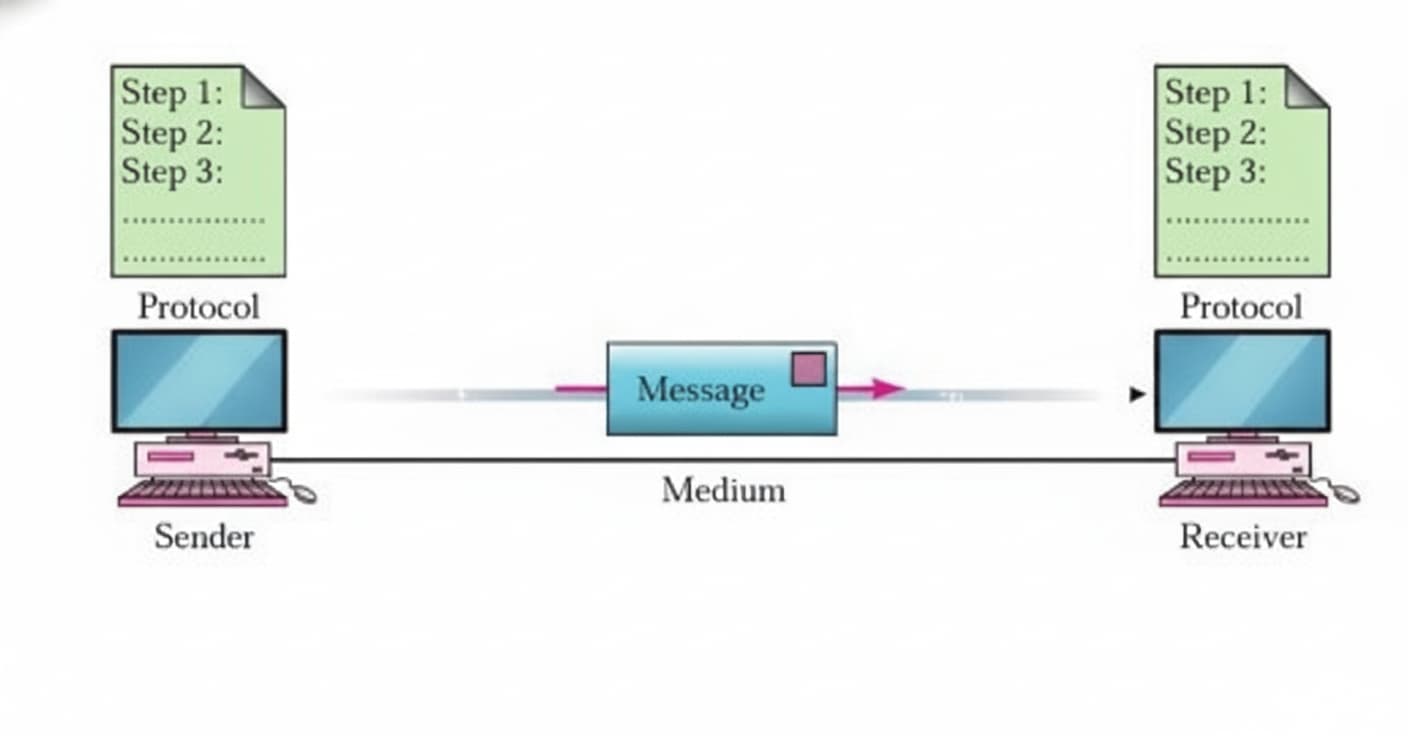
- Sender: The sender is the device that sends the data message.
- Message: The information being shared.
- Medium: The way message is sent (speech, email, phone, signals).
- Receiver: The receiver is the device that receives the message.
- Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules that govern data communications.
Types of Data Communication:
Data communication is the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable. Data Communication has two types :
- Local: Local communication takes place when the communicating devices are in the same geographical area, same building, face-to-face between individuals etc.
- Remote: Remote communication takes place over a distance i.e. the devices are far away from each other.
Fundamental Characteristics Of Data Communication
- Delivery: Delivery should be done to the correct destination.
- Timeliness: Delivery should be on time.
- Accuracy: Data delivered should be accurate.
- Jitter: Variation in packet arrival.
Direction of Data Flow
Direction of Data Flow refers to the way data moves between two devices or processes during communication. It tells who is sending and who is receiving the data.
There are three main types: (also called Transmission Modes)
- Simplex
- Half-Duplex
- Full-Duplex
Basics of Computer Networking
A computer network is a collection of interconnected devices that share resources and information. These devices can include computers, servers, printers, and other hardware. Networks allow for the efficient exchange of data, enabling various applications such as email, file sharing, and internet browsing.
Basic Terminologies of Computer Networks
- Network: A group of connected computers and devices that can communicate and share data with each other.
- Node: Any device that can send, receive, or forward data in a network. This includes laptops, mobiles, printers, earbuds, servers, etc.
- Networking Devices: Devices that manage and support networking functions. This includes routers, switches, hubs, and access points.
- Transmission Media: The physical or wireless medium through which data travels between devices.
- Wired media: Ethernet cables, optical fiber.
- Wireless media: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, infrared
- Service Provider Networks: Networks offered by external providers that allow users or organizations to lease network access and capabilities. This includes internet providers, mobile carriers, etc.
PURPOSE OF A NETWORK
- File and Data Sharing
- Resource Sharing
- Data Protection & Redundancy
- Ease of Administration
- Internal Communications
- Distributing Computing Power
NETWORK CRITERIA
- Performance
- Reliability
- Scalability
- Security
PROPERTIES OF GOOD NETWORK
- Interpersonal Communication : We can communicate with each other efficiently and easily example emails, chat rooms,video conferencing etc.
- Sharing files, data : Authorized users are allowed to share the files on the network.
- Resources can be shared : We can use the resources provided by network such as printers etc.
ADVANTAGES OF NETWORKING
- Connectivity and Communication
- Data Sharing
- Hardware Sharing
- Internet Access
- Internet Access Sharing
- Data Security and Management
- Entertainment
DISADVANTAGES OF NETWORKING
- Network Hardware, Software and SetupCosts
- Hardware and Software Management and Administration Costs
- Undesirable Sharing
- Illegal or Undesirable Behaviour
- Data Security Concerns